Empress
Technical News - December 2010
Empress Database Callable Administration API
Ubiquitous Embedded Database Administration
Introduction
Embedded systems nowadays store more and more data in databases.
With this increase in database deployment, sophisticated database
administration tasks have to be performed on the embedded devices.
However, embedded systems need to keep on working without
interruption or human intervention, so a callable database
administration API is a must have.
Database administration in embedded systems consists of two groups
of tasks, namely 1) initial configuration and 2) ongoing
maintenance. Initial configuration includes database design and
tuning. Ongoing maintenance includes: backup, automatic recovery,
reinitialization of the database from scratch or backup, logging,
data reorganization, data integrity checking and repairing, index
rebuilding, etc.
To address the ever-growing need for smarter and more efficient
database administration in embedded systems, Empress Software has
introduced the Empress Callable Administration API.
Empress Callable Administration API Overview
Empress Callable Administration API has been implemented to provide
similar functionality to standard command line Empress utilities.
Callable Administration API routines may be used in place of
utilities.
The following database administration functionality is supported via
the corresponding callable administration API in the table below.
|
Empress
Administration Functionality
|
Empress
Callable Administration API
|
|
DB
checking and repairing
|
msdbmaintain
|
|
DB export
|
msdbexport
|
|
DB
import
|
msdbimport
|
|
Connectivity
Server Administration
|
mscnsvadm
|
|
DB on-line
backup
|
msdbolbak
|
|
DB
on-line recovery
|
msdbolrec
|
Empress Callable Administration API routines can be run as either tasks or processes and provide additional flexibility to run
database administration tasks for both process and task-based
operating systems.
Figure 1 describes the scenario where the main
application spawns two threads to perform two database tasks. The
first thread executes an Empress task that performs database
retrieval operations while the second thread invokes the Empress
Callable Administration API routine msdbmaintain
execute a database integrity-checking task.
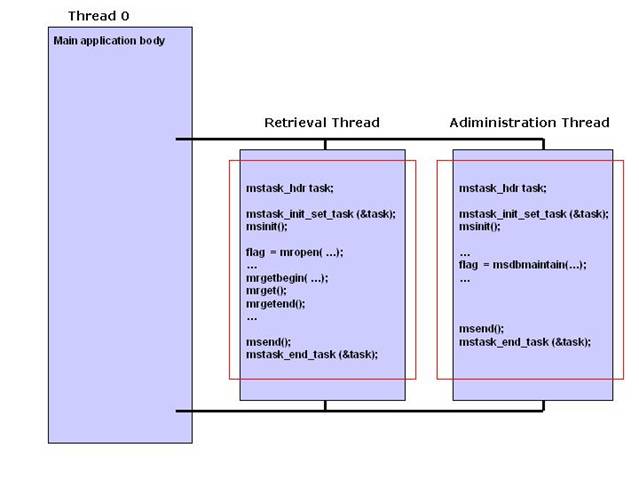
Figure 1: Scenario using Empress Callable Administration API
in a thread
Compiling and Linking with Callable Administration API
In order to compile and link a program that includes
Empress callable Administration API routines, add the option
–utilapi to the Empress compiler utility empcc:
empcc –utilapi example.c
The option –utilapi requires that version of Empress
Database have multi-thread support.
Most embedded operating systems such as Android, Apple iOS, eSOL,
Linux (embedded), Lynx O/S, MontaVista Linux, QNX, T-Engine, Windows
CE, Windows Mobile or VxWorks allow Empress to have multi-thread
support.
Empress Callable Administration API Example
The example program called example.c
is shown below. This program executes the
database checking callable administration API routine msdbmaintain against the database " repairs" .
#include < mscc.h>
#define DATABASE "
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
int status
msbool found_error_and_fix
if (! ())
{
fprintf (stderr, " Unable to
initialize Empress\n" )
msend()
return 1
}
if ( (DATABASE,
false, & status, & found_error_and_fix) != 0)
{
fprintf
(stderr,
"
msdbmaintain () unsuccessful: %s\n" ,
mrerrmsg())
msend()
return 1
}
printf(" DATABASE: %s\n" , DATABASE)
printf(" status: %d\n" , status)
printf(" found_error_and_fix: %d\n" ,
found_error_and_fix)
msend ()
return 0
}
The first parameter in the routine msdbmaintain
is the database that requires checking.
The second parameter in the routine msdbmaintain
(false) invokes a quick
check that involves only 6 default checks (out of 19), namely:
CHECK 1: Recreating shared memory as
necessary
CHECK 2: Find all clients which terminated
improperly
CHECK 3: Check semaphores
CHECK 4: Resolve transactions
CHECK 5: Resolve locks
CHECK 16: Check database coordinator
facility
The third parameter in the routine msdbmaintain status) is the pointer
to the last status of
The fourth parameter in the routine msdbmaintain
(&
found_error_and_fix) is the
pointer (msbool*
that shows whether msdbmaintain
problems and fixed them. If the value is it
shows it found problems and fixed them. If the value is false
it shows it didn’t find problems.
Instead of Summary
To address the ever-growing need for smarter and more efficient
database administration in embedded systems, anywhere and
everywhere, Empress Software has provided Empress Callable
Administration API. Empress Callable Administration API is
implemented to provide database checking and
repairing, server administration or backup. These complex
tasks that are typically run by a database administration of the
enterprise database system can now be automated for embedded systems
making them truly ubiquitous.
Empress Software Inc.
www.empress.com